Transforming Surgery: How Augmented Reality Revolutionizes Precision in Complex Procedures
The Evolution of Surgical Precision
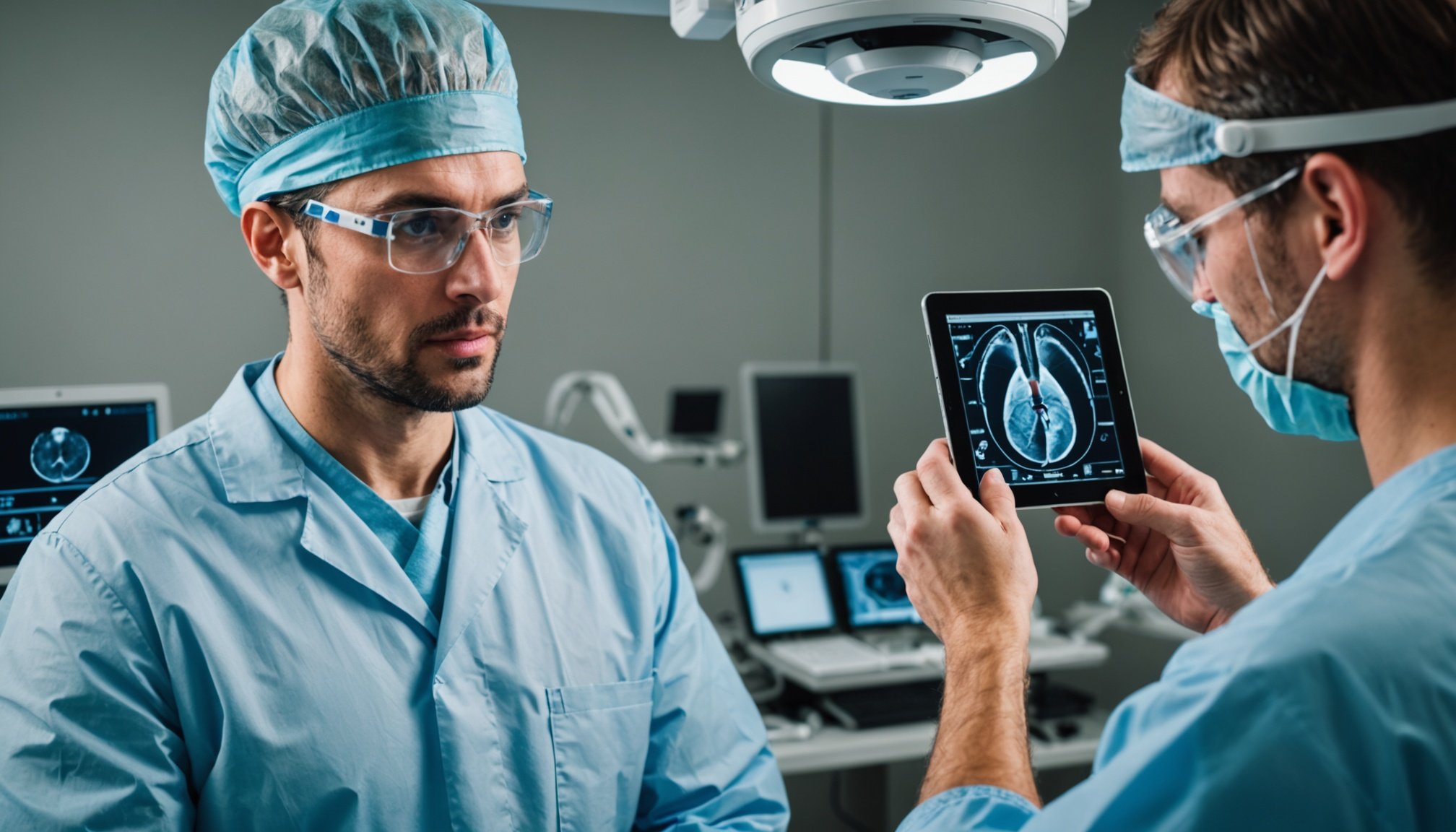
Surgery, a field that has been at the forefront of medical innovation, is undergoing a significant transformation with the integration of augmented reality (AR). This technology is not just a novelty; it is a game-changer that enhances precision, safety, and efficiency in surgical procedures. In this article, we will delve into how AR is revolutionizing the surgical landscape, particularly in complex procedures like spine surgery.
Understanding Augmented Reality in Surgery
Augmented reality is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the real-world environment. In the context of surgery, AR superimposes 3D images of a patient’s anatomy onto the surgeon’s visual field during the procedure. This is achieved through advanced imaging techniques and specialized headsets.
Additional reading : Transforming city waste management: how iot technology enhances efficiency in urban environments
How AR Works in Surgical Navigation
In surgical navigation, AR uses preoperative CT scans or MRI images to create a detailed 3D model of the patient’s anatomy. During the surgery, this model is superimposed onto the patient’s body, providing the surgeon with real-time guidance. Here’s a step-by-step look at how this process works:
- Preoperative Planning: Surgeons use advanced software to plan the surgery, identifying the exact locations for incisions and implant placements.
- Intraoperative Guidance: The AR system overlays the preoperative plan onto the patient’s anatomy in real time, allowing the surgeon to see the precise location of anatomical structures and implants.
- Real-Time Feedback: The system provides continuous feedback, ensuring that the surgeon stays on track and makes adjustments as necessary.
Comparative Analysis: Robotic-Assisted Navigation vs. Augmented Reality
A recent study at the Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) compared the precision and safety of robotic-assisted navigation (RAN) and AR in spine surgery. Here are the key findings:
In parallel : Transforming customer support with ai: unveiling the latest trends and innovations
Study Overview
- Participants: 212 adult patients underwent lumbar or sacral spine surgery for degenerative conditions between June 2020 and October 2023.
- Techniques: 108 patients received 827 pedicle screws using RAN, while 104 patients received 384 screws using AR.
- Evaluation: The accuracy of screw placement was assessed using the Gertzbein-Robbins classification system, with Grades A and B considered acceptable[1][2][4].
Key Findings
| Technique | Number of Screws | Grade A or B Accuracy | Grade A Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAN | 827 | 99.6% | Higher proportion |
| AR | 384 | 98.7% | 92.6% overall |
Quotes from Dr. Darren R. Lebl, MD, MBA:
- “Compared to conventional free-hand techniques, both robotic-assisted navigation and the use of augmented reality have demonstrated superior accuracy.”
- “Our results confirmed excellent accuracy for both techniques, making both robotics and AR safe tools for accurate positioning of lumbosacral pedicle screws.”
Benefits of Augmented Reality in Surgery
The integration of AR in surgical procedures offers several significant benefits:
Enhanced Precision
AR provides surgeons with real-time, precise anatomical information, reducing the risk of errors and improving the accuracy of implant placements.
Reduced Radiation Exposure
Both AR and RAN technologies minimize the need for intraoperative radiation, which is a significant advantage for patient safety and long-term health outcomes[1][2].
Improved Safety
By providing continuous real-time feedback, AR enhances the safety of surgical procedures, allowing surgeons to make more informed decisions during the operation.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
AR enables surgeons to perform minimally invasive surgeries with greater precision, leading to smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and faster recovery times.
Training and Education with Augmented Reality
AR is not only transforming surgical procedures but also revolutionizing medical education and training.
Augmented Reality Training
Surgeons can now practice complex procedures in a simulated environment using AR. This approach enhances their skills and confidence before performing real surgeries.
Example:
Dr. Joseph Tauro’s work at the MAST conference highlighted how AR can improve the precision, efficiency, and safety of arthroscopic procedures through innovative training methods[5].
Real-World Applications
AR training programs are designed to mimic real-world scenarios, allowing surgeons to practice and perfect their techniques in a controlled environment. This includes preoperative planning, surgical navigation, and postoperative care.
The Future of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
As AR technology continues to evolve, its potential in healthcare is vast and promising.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The combination of AR with artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to further enhance surgical precision and decision-making. AI can analyze real-time data and provide predictive insights, helping surgeons make more accurate and timely decisions.
Voice-Controlled User Interfaces
Recent studies have introduced voice-controlled user interfaces (VCUIs) for AR systems, which can reduce cognitive workload and improve task execution times. This technology, integrated with large language models (LLMs), shows significant promise in making AR more intuitive and efficient[3].
Practical Insights and Actionable Advice
For those interested in the adoption and integration of AR in surgical practices, here are some practical insights:
Investment in Technology
Hospitals and medical centers should invest in advanced AR systems and training programs to ensure that surgeons are equipped with the latest technologies.
Continuous Training
Surgeons should participate in regular training sessions to stay updated with the latest AR technologies and techniques.
Patient Education
Patients should be educated about the benefits and risks of AR-assisted surgeries to make informed decisions about their care.
Augmented reality is transforming the field of surgery by enhancing precision, safety, and efficiency. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of revolutionizing healthcare outcomes and redefining the future of surgical procedures. Whether through robotic-assisted navigation or AR, the integration of these technologies is set to make surgeries safer, less invasive, and more precise, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
Table: Comparative Benefits of RAN and AR in Spine Surgery
| Benefit | Robotic-Assisted Navigation (RAN) | Augmented Reality (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High accuracy (99.6% Grade A or B) | High accuracy (98.7% Grade A or B) |
| Radiation Exposure | Reduced | Reduced |
| Safety | Enhanced safety with real-time feedback | Enhanced safety with real-time feedback |
| Minimally Invasive | Yes | Yes |
| Training Requirements | Advanced software and robotic training | AR headset and preoperative planning |
| Real-Time Feedback | Yes | Yes |
| Surgeon Experience | Requires experienced surgeons | Requires experienced surgeons |
Detailed Bullet Points: Key Advantages of AR in Surgery
-
Enhanced Precision:
-
Real-time anatomical information
-
Reduced risk of errors
-
Improved accuracy of implant placements
-
Reduced Radiation Exposure:
-
Minimized need for intraoperative radiation
-
Improved patient safety and long-term health outcomes
-
Improved Safety:
-
Continuous real-time feedback
-
Informed decision-making during surgery
-
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
-
Smaller incisions
-
Less tissue damage
-
Faster recovery times
-
Advanced Training:
-
Simulated environments for practice
-
Enhanced skills and confidence for surgeons
-
Real-world scenario simulations
-
Integration with AI:
-
Analyzing real-time data
-
Providing predictive insights
-
Enhancing surgical precision and decision-making
-
Voice-Controlled User Interfaces:
-
Reducing cognitive workload
-
Improving task execution times
-
Integrating with large language models (LLMs) for more intuitive AR systems